Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Services Without Domain
- Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Services Without Domain Names
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Server 2016
- Cached
Home > Sample chapters

Select the computer as the destination server. On the Select server roles page, select Remote Desktop Services. On the Select role services page, select the Remote Desktop Licensing and Remote Desktop Session Host role services. ' Any RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of Remote Desktop Services and the current version of Remote Desktop Services. For example, a Windows Server 2016 RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of RDS, while a Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS license server can only host licenses up to Windows. The basic requirement is to have access to all Remote Desktop Services, including RD licensing, RD Web Access etc. Without configuring the server as a Domain Controller and Active Directory.
Remote Desktop Services Windows 2016 No Domain Controller Background: Just trying to see if I can get a succinct answer to whether I can run a remote desktop service (RDS) on Windows 2016 without having a Domain/Active Directory setup. When we set up a new Windows Server, a default Administrator account is created for us. While this is fine initially, you should always create a separate user for day to day purposes. In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a new user in Windows Server 2016 and allow it to use RDP (Remote Desktop.
- 7/15/2011
 Contents×
Contents×- Before You Begin
You can use VPNs to allow remote users to connect to your organization’s internal network resources, whether they are using a hotel wireless hotspot in Gundagai or are connecting through an ADSL connection in Canberra. When you plan how to provision VPN access, you need to take into account a host of factors. You need to know how your organization’s external firewall will be configured, the operating system used by the client, and the types of resources that remote clients will need to access.
Network Access Protection (NAP) allows you to restrict network access on the basis of client health. Put simply, NAP allows you to enforce a rule that if the client is not up to date with patches and antivirus definitions, you can block it from getting full access to the network. In this chapter, you will learn how to configure and deploy NAP and the various methods that are available to deal with noncompliant computers. You will also learn how to plan and deploy Windows Server 2008 R2 remote access services to ensure that your organization’s clients can connect to your internal resources no matter where in the world they are.
Exam objectives in this chapter:
Plan infrastructure services server roles.
Monitor and maintain security and policies.
Lessons in this chapter:
Lesson 1: Managing Remote Access
Lesson 2: Firewalls and Network Access Protection
Before You Begin
To complete the exercises in the practice in this chapter, you need to have done the following:
Complete the setup tasks outlined in Appendix A, “Setup Instructions for Windows Server 2008 R2.”
No additional configuration is required for this chapter.
This chapter is from the book
Related resources
- By Daniel A. Seara, Francesco Milano
- Book $39.99
- By Daniel A. Seara, Francesco Milano
- eBook (Watermarked) $31.99
- By Joan Lambert
- Book $24.99
I have seen so many deployments of RDS (Remote Desktop Services) done incorrectly in Windows Server 2012/2012R2 that I wanted to get the correct process out there. Unlike previous versions of Windows, RDS in 2012 must be deployed with the RDS installation wizard. There is one exception to this rule. When there is only one server and it is in a workgroup, the deployment works differently. I will cover that deployment in another guide.
Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Services Without Domain Names
This guide is applicable for a Windows 2012/2012R2 server that is joined to a domain or is a domain controller. Following the below steps will take you through the setup of the first RDS server.
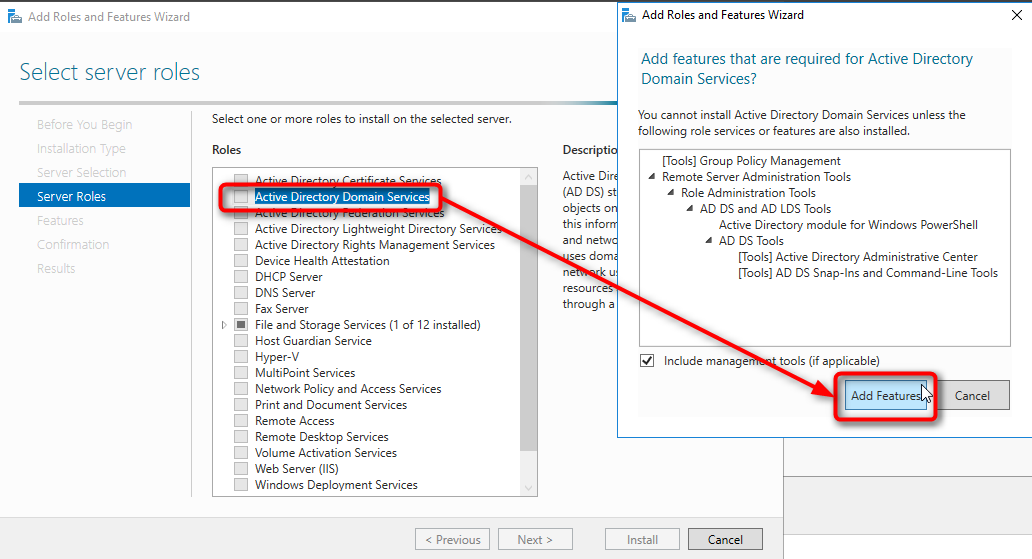
- Join the server to the domain. If the server is also to be the domain controller*, install the ADDS (Active Directory Domain Services) role and promote the server.
- Launch the Add Roles and Features Wizard in Server Manager.
- Launch Server Manager
- At the top right, click Manage
- Choose Add Roles and Features
- On the Installation Type screen, choose Remote Desktop Services installation and click Next.
- On the Deployment Type screen, choose Quick Start and click Next.
- On the Deployment Scenario screen, choose Session-based desktop deployment and click Next
- On the Server Selection screen, verify the server is selected and click Next.
- On the Confirmation screen, check the box to Restart the destination server automatically if required and click Deploy. The server will automatically reboot.
- Log into the server after the reboot. The wizard will automatically launch and the deployment should complete. Close the wizard when complete.
- Go back to Server Manager. On the left side click on Remote Desktop Services. You should see a screen similar to the following.
- Click the + symbol above RD Licensing. This will launch the wizard to add a licensing server.
- Add the server to the Selected list and click Next.
- Click Add. When the process completes, click Close
- Click the TASKS button next to DEPLOYMENT OVERVIEW and choose the option to Edit Deployment Properties.
- Click the RD Licensing option on the left side. Choose the licensing mode that matches the RDS CALs purchased. The licensing server should already be populated. If it is not type in the FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) and click Add. Click OK.
Microsoft Remote Desktop Server 2016
You now have a very basic setup of Remote Desktop Services. The next step is to activate your license server and install your RDS CALs. I will write an article on that process in the near future and update this article once it is published.
Cached
*Microsoft discourages making an RDS server a domain controller. If it is required, see this technet article.
